Verify DKIM Records for Enhanced Email Security
DKIM Record Checker
| DKIM Record |
|---|
Superior support
MailProvider's dedicated support team is available 24/7, ensuring you never miss a beat.
Hosted in Luxembourg
MailProvider uses advanced security measures to protect your accounts from any potential threats or attacks.
Guaranteed email delivery
With MailProvider's flawless IP reputation, your emails are guaranteed to reach their destination seamlessly.

Im more than happy to help you setup your SPF records according to the highest standards.
Paige Lowery, Support Hero
DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail) Inquiry
You can use DKIM challenge to verify that your domain's DNS servers are sending back your DKIM record correctly.
To perform the query, enter your domain name and DKIM selector in the query field above and click the query button.
Some of our other free email tools
SPF Checker
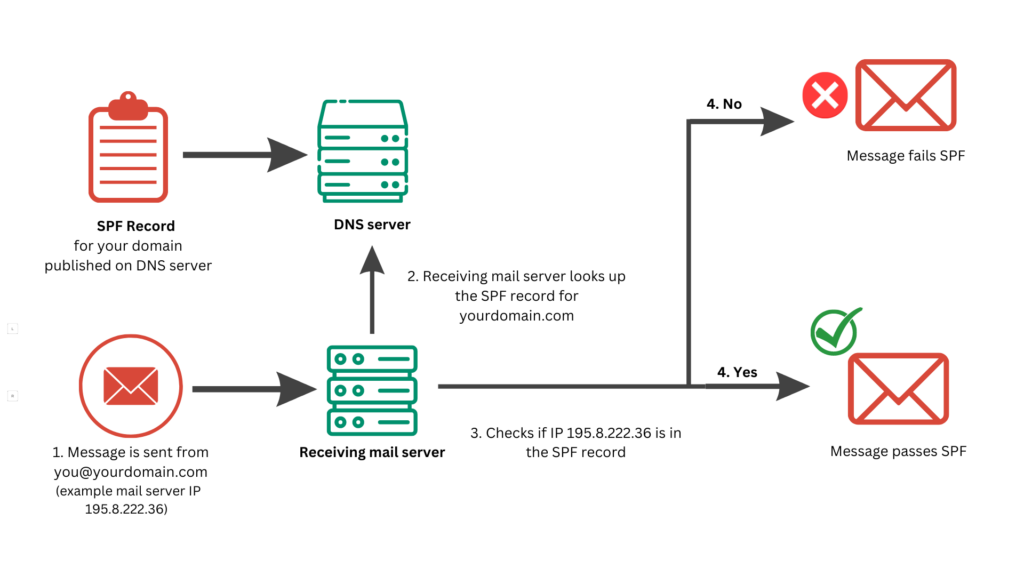
SPF Checker is a tool that verifies whether a domain's SPF (Sender Policy Framework) record is correctly configured to prevent email spoofing.
SPF Record Creator
SPF Record Creator is a tool that helps generate the correct SPF record for a domain to authorize specific mail servers to send emails on its behalf.
Mx Record Checker
MX Record Checker is a tool that verifies and retrieves the Mail Exchange (MX) records of a domain to ensure proper email delivery setup.
DKIM Record Checker
DKIM Record Checker is a tool that validates the presence and correctness of a domain's DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) record to ensure email authentication and integrity.
DMARC Record Checker
This is a tool that verifies the existence and validity of a domain's DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) record to ensure email authentication and policy enforcement.
Whois Domain Checker
Whois Domain Checker is a tool that retrieves detailed information about a domain's ownership, registration, and expiration status by querying the Whois database.
NS Checker
NS Checker is a tool that verifies the nameserver (NS) records for a domain to ensure proper DNS configuration and resolution.
Mail Blacklist Checker
Mail Blacklist Checker is a tool that checks if an IP address or domain is listed on any email blacklists, which can affect email deliverability and reputation.
IP Address Checker
IP Address Checker is a tool that provides information about a specific IP address, including its location, ISP, and other relevant details.
Secure email that
protects your privacy
Help Center
Questions? Answers.
Quick answers to questions you may have. Can't find what you're looking for? Check out our full documentation.
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) is an email authentication method designed to detect forged sender addresses. It works by attaching a digital signature to the headers of an email. This signature is generated with a private cryptographic key and can be verified by recipients using the corresponding public key, which is published in the domain's DNS. DKIM helps ensure that an email has not been altered and that it truly comes from the claimed domain.
To create a DKIM record:
- Generate a private-public key pair using a tool like OpenDKIM or a similar service.
- Store the private key on your mail server to sign outgoing emails.
- Publish the public key as a TXT record in your domain’s DNS with a format like
selector._domainkey.yourdomain.com, whereselectoris a custom string used to differentiate multiple keys. - The TXT record will contain the public key and look something like:
v=DKIM1; k=rsa; p=YourPublicKey. - Save your DNS changes and ensure your email server is properly configured to use the private key for DKIM signing.
A DKIM record provides the public key needed to verify the digital signature on an email. This authentication mechanism helps protect against email tampering and spoofing by ensuring that the email's contents and sender domain have not been altered during transmission. DKIM records also improve email deliverability by helping emails pass anti-spam filters.
To query DKIM records using the dig command, you need to specify the selector and the domain. The format is:
dig TXT selector._domainkey.yourdomain.com
For example, if the selector is default and the domain is example.com, the query would be:
dig TXT default._domainkey.example.com
This will return the DKIM public key stored in the DNS.
DKIM and SPF (Sender Policy Framework) are both email authentication methods, but they operate differently:
- SPF works by defining which mail servers are authorized to send emails on behalf of a domain. It uses a TXT record in the DNS to list these servers.
- DKIM, on the other hand, adds a digital signature to the email that can be verified using the public key published in the DNS. It ensures the integrity of the email’s content and its origin.
SPF focuses on validating the sender’s IP, while DKIM focuses on validating the email's content.
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) builds on both SPF and DKIM by providing a policy to handle email authentication failures and reporting. While DKIM ensures that an email hasn't been altered and verifies the sender, DMARC adds an additional layer by instructing email receivers on what to do if SPF and/or DKIM checks fail (e.g., reject, quarantine, or allow the email). DMARC also sends feedback reports to the domain owner for monitoring authentication results.
To update a DKIM record:
- Access your domain’s DNS management.
- Locate the current DKIM TXT record (usually in the format
selector._domainkey.yourdomain.com). - Edit the value to replace the existing public key with a new one.
- Save the changes, and allow DNS propagation.
Make sure to also update your mail server’s private key to match the new public key.
To disable DKIM for your domain:
- Remove the DKIM TXT record from your DNS, which stops recipients from verifying DKIM signatures.
- Additionally, disable DKIM signing on your mail server by removing or deactivating the DKIM private key configuration.
Once disabled, your outgoing emails will no longer be signed with DKIM, and recipients will not be able to authenticate your emails using DKIM.
Here’s an example of a DKIM TXT record:
default._domainkey.example.com IN TXT "v=DKIM1; k=rsa; p=MIGfMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBAQUAA4GNADCBiQKBgQDg1+JJ3yxiJcA..."
default: This is the DKIM selector.v=DKIM1: Indicates the DKIM version.k=rsa: Specifies the key type (RSA).p=...: The public key used to verify the signature.
Yes, a DKIM signature is important because it helps authenticate an email's origin and ensures that the message has not been tampered with during transit. It builds trust in email communications, improves email deliverability, and protects against email spoofing and phishing attacks. Many email services and spam filters give preference to DKIM-signed emails.
A DKIM signature is a cryptographic signature added to the email headers that verifies the integrity of the message. It is generated using the sender’s private key and validated using the corresponding public key in the DKIM record. It looks like this in the email headers:
DKIM-Signature: v=1; a=rsa-sha256; d=example.com; s=default;
h=from:to:subject:date;
bh=47DEQpj8HBSa+/TImW+5JCeuQeRkm5NMpJWZG3hSuFU=;
b=NJfPR7TX...;
d=example.com: The domain that signed the email.s=default: The DKIM selector.bh: Hash of the email body.b: The actual DKIM signature.
o add the "DKIM-Signature" header to your outgoing emails, you need to configure your email server to sign outgoing emails with DKIM:
- Generate a DKIM key pair (public and private keys).
- Publish the public key as a TXT record in your DNS (under
selector._domainkey.yourdomain.com). - Configure your mail server to use the private key for signing outgoing emails (commonly done through software like OpenDKIM, Postfix, or cPanel settings).
- Once configured, your mail server will automatically add the “DKIM-Signature” header to outgoing emails.
