Understanding Brute Force Attacks: What They Are and How to Prevent Them
In the realm of cybersecurity, one of the most common and straightforward methods employed by attackers is the brute force attack. This blog post will explore what brute force attacks are, how they work, and the best practices to prevent them.
What is a Brute Force Attack?
A brute force attack is a trial-and-error method used to obtain information such as passwords, encryption keys, or personal identification numbers (PINs). Attackers systematically attempt every possible combination of characters until they find the correct one. While this approach can be time-consuming, advancements in computing power and the availability of automated tools have made it increasingly effective.
How Brute Force Attacks Work
Brute force attacks typically involve the following steps:
- Target Selection: The attacker identifies a target system, which could be a website, server, or application.
- Tool Acquisition: Attackers utilize automated tools or scripts designed to generate and test numerous password combinations rapidly.
- Attack Execution: The tool sends requests to the target system, attempting different combinations of usernames and passwords.
- Successful Entry: If the attacker guesses the correct password, they gain unauthorized access to the target.
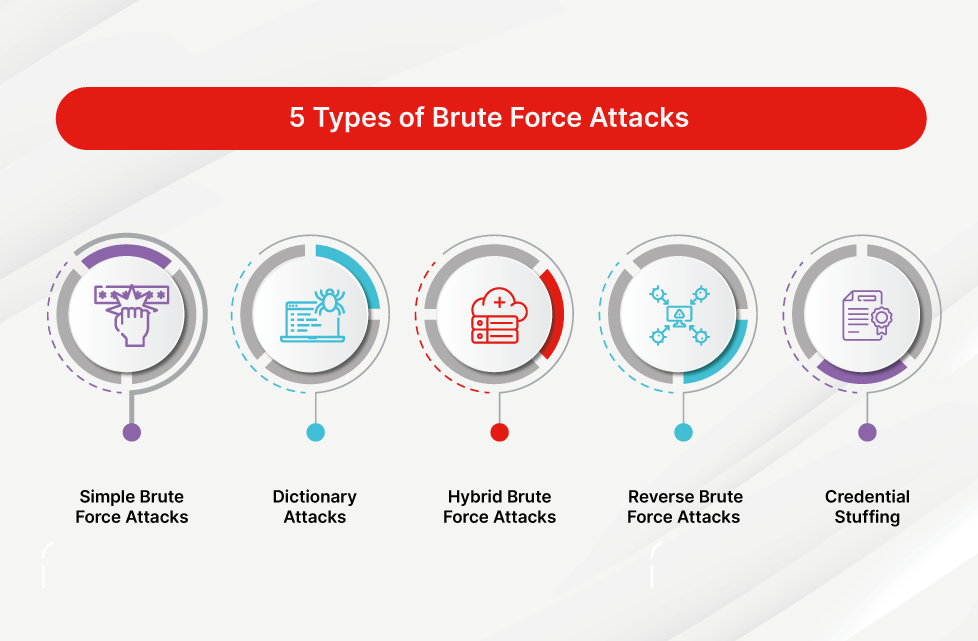
There are various types of brute force attacks, including:
- Simple Brute Force: Trying all possible combinations until the correct one is found.
- Dictionary Attack: Using a predefined list of common passwords or phrases to guess the password.
- Hybrid Attack: A combination of dictionary and brute force methods, where common passwords are modified with numbers or symbols.
Why Brute Force Attacks Are a Threat
- Ease of Execution: Brute force attacks require minimal skill and can be performed using readily available tools.
- Automation: Attackers can automate the process, making it faster and more efficient than manual attempts.
- Weak Passwords: Many users still use weak or common passwords, making them easy targets for brute force attacks.
How to Prevent Brute Force Attacks
1. Implement Strong Password Policies
Encourage users to create strong, unique passwords that are difficult to guess. A strong password typically includes:
- A minimum of 12 characters
- A mix of uppercase and lowercase letters
- Numbers and special characters
- Avoiding easily guessable information (e.g., birthdays, names)
2. Enable Account Lockout Mechanisms
Implement account lockout policies that temporarily disable accounts after a certain number of failed login attempts. This discourages attackers from attempting numerous combinations without consequences.
3. Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an additional layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to an account. Even if a password is compromised, an attacker would need the second factor to access the account.
4. Limit Login Attempts
Limit the number of login attempts allowed within a specified time frame. After reaching the limit, users should be temporarily locked out or required to complete a CAPTCHA challenge to proceed.
5. Monitor Login Activity
Regularly review login attempts and monitor for suspicious activity, such as multiple failed login attempts from the same IP address. Implement alerts for potential brute force attempts to respond quickly.
6. Utilize CAPTCHAs
Incorporating CAPTCHAs on login forms can help prevent automated tools from submitting login requests, making it more difficult for attackers to perform brute force attacks.
7. Educate Users
User awareness is key in preventing brute force attacks. Provide training on the importance of strong passwords, recognizing phishing attempts, and using password managers to store credentials securely.
Conclusion
Brute force attacks pose a significant threat to individuals and organizations alike. By understanding how these attacks work and implementing the prevention strategies outlined above, you can safeguard your accounts and sensitive information. Remember that cybersecurity is an ongoing process that requires vigilance and proactive measures.
