Check DMARC Records to Prevent Email Spoofing
DMARC Record Scanner
| DMARC Record |
|---|
Superior support
MailProvider's dedicated support team is available 24/7, ensuring you never miss a beat.
Hosted in Luxembourg
MailProvider uses advanced security measures to protect your accounts from any potential threats or attacks.
Guaranteed email delivery
With MailProvider's flawless IP reputation, your emails are guaranteed to reach their destination seamlessly.

Im more than happy to help you setup your SPF records according to the highest standards.
Paige Lowery, Support Hero
DMARC Records
Prefent email spoofing
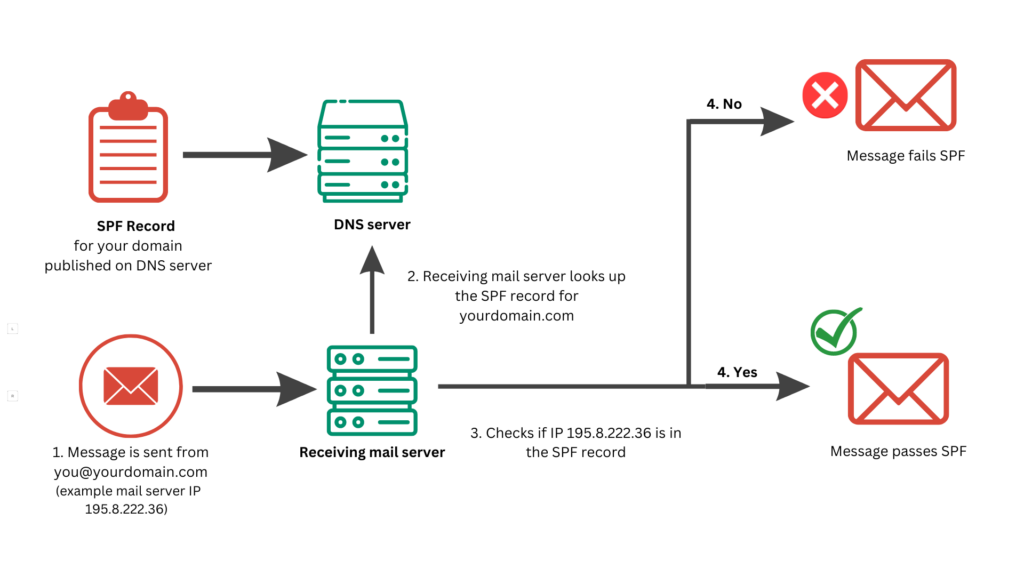
You can use a DMARC challenge to verify that your domain's DNS servers are correctly sending back your DMARC record.
To perform the query, enter your domain name in the query field above and click the query button.
Some of our other free email tools
SPF Checker
SPF Checker is a tool that verifies whether a domain's SPF (Sender Policy Framework) record is correctly configured to prevent email spoofing.
SPF Record Creator
SPF Record Creator is a tool that helps generate the correct SPF record for a domain to authorize specific mail servers to send emails on its behalf.
Mx Record Checker
MX Record Checker is a tool that verifies and retrieves the Mail Exchange (MX) records of a domain to ensure proper email delivery setup.
DKIM Record Checker
DKIM Record Checker is a tool that validates the presence and correctness of a domain's DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) record to ensure email authentication and integrity.
DMARC Record Checker
This is a tool that verifies the existence and validity of a domain's DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) record to ensure email authentication and policy enforcement.
Whois Domain Checker
Whois Domain Checker is a tool that retrieves detailed information about a domain's ownership, registration, and expiration status by querying the Whois database.
NS Checker
NS Checker is a tool that verifies the nameserver (NS) records for a domain to ensure proper DNS configuration and resolution.
Mail Blacklist Checker
Mail Blacklist Checker is a tool that checks if an IP address or domain is listed on any email blacklists, which can affect email deliverability and reputation.
IP Address Checker
IP Address Checker is a tool that provides information about a specific IP address, including its location, ISP, and other relevant details.
Secure email that
protects your privacy
Help Center
Questions? Answers.
Quick answers to questions you may have. Can't find what you're looking for? Check out our full documentation.
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) is an email authentication protocol that helps protect email senders and recipients from spoofing and phishing attacks. It allows domain owners to specify which mechanisms (like SPF and DKIM) are used to authenticate their emails and provides instructions on how to handle emails that fail authentication checks.
To create a DMARC record, you need to add a TXT record to your domain's DNS settings. Here’s how to do it:
- Log in to your domain registrar’s control panel.
- Navigate to the DNS management section.
- Add a new TXT record with the name
_dmarc.yourdomain.com. - In the value field, include your DMARC policy, e.g.,
v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:[email protected];. Replaceyourdomain.comwith your actual domain. - Save the changes and allow time for DNS propagation.
A DMARC record helps:
- Authenticate emails sent from your domain to prevent spoofing.
- Provide feedback on the email authentication process through reports.
- Control how email receivers handle emails that fail authentication checks (e.g., reject, quarantine, or do nothing).
To update a DMARC record, log in to your domain registrar’s control panel and navigate to the DNS management section. Locate the existing DMARC TXT record (usually named _dmarc.yourdomain.com) and edit the value to reflect your new DMARC policy. Save the changes, and wait for the updates to propagate.
DMARC record tags are parameters within a DMARC TXT record that define the policy and reporting settings. Common tags include:
v: Version of DMARC (must beDMARC1).p: Policy for handling failed emails (none,quarantine, orreject).rua: Email address for aggregate report submissions.ruf: Email address for forensic report submissions.sp: Subdomain policy (similar top, but for subdomains).
To receive DMARC reports, you need to include the rua (for aggregate reports) and/or ruf (for forensic reports) tags in your DMARC record. Specify an email address where you want the reports sent. After implementing DMARC, you will begin receiving reports from email providers regarding the authentication status of your emails.
DMARC reports should be reviewed by domain administrators, email marketers, and security teams. These reports provide insights into email authentication issues and can help in fine-tuning email sending practices to enhance security and deliverability.
To effectively manage DMARC reports, consider creating a dedicated email address or group mailbox (e.g., [email protected]) to receive and analyze the reports. This helps keep your main inbox free from clutter and allows for more organized handling of DMARC data.
To disable DMARC for your domain, you can either remove the DMARC TXT record from your DNS settings or change the policy tag (p) in the record to p=none. This tells receiving servers to take no action on emails that fail authentication checks, effectively disabling DMARC enforcement.
Email security is crucial because email is a common vector for cyber attacks, including phishing, spoofing, and malware distribution. Protecting your email communications helps safeguard sensitive information, maintain trust with customers and partners, and prevent financial losses associated with fraud and data breaches.
DMARC is important because it provides a way to prevent unauthorized use of your domain in email communications, enhancing email security. It helps protect your brand’s reputation, improves email deliverability by ensuring legitimate emails reach recipients, and provides visibility into email authentication issues through reporting.
While DMARC significantly reduces the risk of phishing attacks by preventing unauthorized email spoofing, it does not eliminate all phishing threats. Attackers can still use other techniques, such as social engineering. DMARC should be part of a broader email security strategy that includes SPF, DKIM, user education, and advanced threat detection.
Sure! An example of a DMARC record might look like this:
_dmarc.example.com. IN TXT "v=DMARC1; p=quarantine; rua=mailto:[email protected]; ruf=mailto:[email protected]; sp=none; aspf=r"
This record specifies that emails failing authentication checks should be quarantined, and aggregate and forensic reports will be sent to the specified email addresses.
