What is a WAF (Web Application Firewall)? A Comprehensive Guide
In an age where cyber threats are increasingly sophisticated, securing web applications has never been more critical. One of the most effective tools in a developer’s and security professional’s arsenal is a Web Application Firewall (WAF). This blog post will explore what a WAF is, how it works, its benefits, and its common use cases.
What is a Web Application Firewall (WAF)?
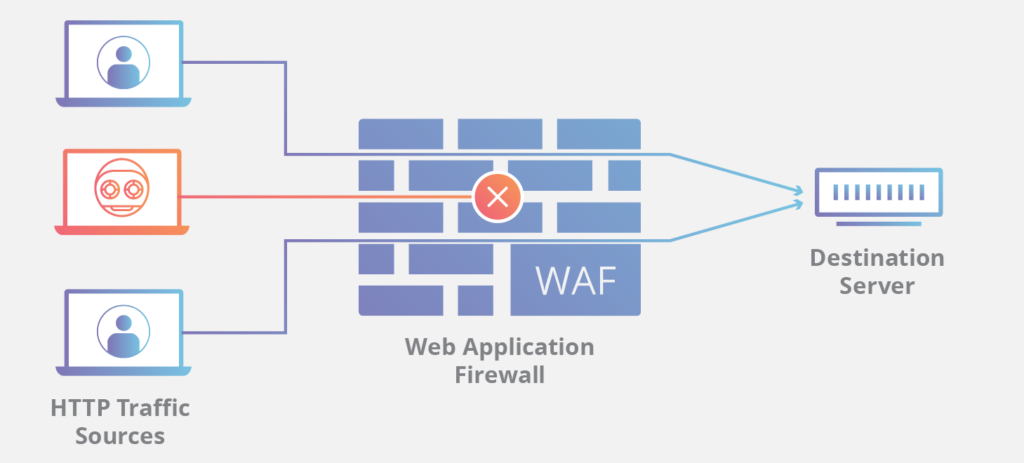
A Web Application Firewall (WAF) is a security solution that monitors, filters, and analyzes HTTP traffic between a web application and the Internet. Unlike traditional firewalls that focus on network security at the transport layer, a WAF operates at the application layer (Layer 7 of the OSI model). It protects web applications by detecting and blocking malicious traffic and protecting against various threats, including SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks.
How Does a WAF Work?
A WAF functions as a shield between a web application and the Internet, intercepting all incoming and outgoing traffic. Here’s how it generally works:
- Traffic Monitoring: The WAF inspects incoming requests to the web application and outgoing responses to users. It analyzes HTTP/HTTPS requests to identify potentially harmful payloads.
- Rules and Policies: The WAF uses pre-defined rules and policies to determine whether to allow or block specific requests. These rules can be customized based on the unique needs of the web application and the threats it faces.
- Threat Detection: By analyzing traffic patterns and signatures, the WAF can detect anomalies or known attack vectors. It can differentiate between legitimate traffic and malicious requests.
- Response Actions: When a potential threat is detected, the WAF can take various actions, such as blocking the request, redirecting users to an error page, or logging the incident for further analysis.
- Reporting and Alerts: WAFs often include reporting features that provide insights into traffic patterns, detected threats, and the effectiveness of security measures, allowing administrators to fine-tune their security posture.
Benefits of Using a WAF
- Enhanced Security: A WAF provides a robust layer of security against common web application vulnerabilities and cyber threats, helping to protect sensitive data.
- Compliance: Many industries are subject to regulations that require specific security measures. A WAF can assist organizations in achieving compliance with standards such as PCI DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR.
- Customizable Rules: WAFs offer the ability to create tailored rules and policies to fit the specific needs of your web application, allowing for more effective threat detection.
- Reduced Downtime: By blocking malicious traffic before it reaches your web application, a WAF can help prevent downtime caused by attacks, ensuring your application remains available to users.
- Protection Against Zero-Day Vulnerabilities: WAFs can provide protection against new and unknown vulnerabilities by applying generic security rules to incoming traffic.
Common Use Cases for WAF
- E-commerce Websites: Online stores are prime targets for cyber attacks. A WAF can help protect payment information, customer data, and ensure compliance with payment security standards.
- Financial Institutions: Banks and financial services use WAFs to secure online banking applications and protect sensitive financial data from theft and fraud.
- Healthcare Applications: WAFs help healthcare organizations safeguard patient data and comply with regulations such as HIPAA.
- SaaS Providers: Software as a Service (SaaS) companies utilize WAFs to protect their applications from various web threats, ensuring the security of their user data.
- Government Websites: Government sites often contain sensitive information and are frequent targets for hackers. WAFs help maintain the security and integrity of these sites.
Conclusion
A Web Application Firewall (WAF) is an essential security solution for any organization that relies on web applications. By offering a robust layer of protection against various cyber threats, WAFs help maintain the integrity, availability, and confidentiality of sensitive data. As cyber threats continue to evolve, implementing a WAF is a proactive step towards enhancing your organization’s overall security posture.
